Amazon Flywheel Effect
The Engine of Long-Term Growth
Welcome to my 29th blog post! Click here to read more from previous posts.
Over nearly last 30 years, Amazon has risen from an online bookstore in 1994 to a global empire reshaping retail, cloud computing, entertainment, and beyond. The question that often arises is, what exactly powers this remarkable success?
The answer lies in the concept of the "Flywheel Effect" which was originally introduced by Jim Collins in his book "Good To Great". Jeff Bezos masterfully applied and executed this concept, also known as the Virtuous Cycle, to propel Amazon's growth.
In this blog post, we will delve into the components of Amazon's flywheel to gain insight into the key factors behind the company's extraordinary growth and uncover the driving force that has made Amazon the global powerhouse it is today.
The Flywheel Effect
Imagine you are assigned a task to move a big and heavy flywheel towards as fast as possible. Initially, the effort feels immense, and progress seems almost non-existent. It can easily make you feel frustrated and even quit this task. But if you persist and keep pushing consistently, something remarkable happens. The flywheel gains momentum, and its spinning speed accelerates. Suddenly, the once-challenging task becomes smoother, and the flywheel runs with ease.
From this analogy, the “Flywheel Effect” has become the popular business concept originated from Jim Collins’ book “Good To Great”. It represents the idea that sustained success and growth result from consistent, focused efforts and positive feedback loops, similar to a heavy flywheel gaining momentum with each turn.
In the quest for success, companies often seek groundbreaking innovations or overnight triumphs. However, the reality is that sustained success is built upon creating positive feedback loops from incremental small wins accumulated over time. Once the momentum is attained, growth appears to happen almost effortlessly. Amazon is a prime example of harnessing the Flywheel Effect, benefiting not only the company itself but, more importantly, its customers through the efficient network effect.
However, it's essential to note that the flywheel can lose momentum and slow down when companies make frequent dramatic changes in direction without consistent effort. This phenomenon, known as the "Doom Loop," was also highlighted by Collins in his book. Interestingly, the "Flywheel Effect" and the "Doom Loop" can occur simultaneously within a company if it fails to understand the critical components that enabled the flywheel's initial success and makes rash alterations.
A case in point is Nokia, which experienced both the "Flywheel Effect" and the "Doom Loop." While the company enjoyed the positive flywheel effect from its strong brand reputation and distribution network, it simultaneously faced the doom loop due to neglecting innovation and failing to adapt to customers' shift towards smartphones during 2007 to 2011. This combination led to the downfall of the once-mobile phone giant.
The Amazon Flywheel
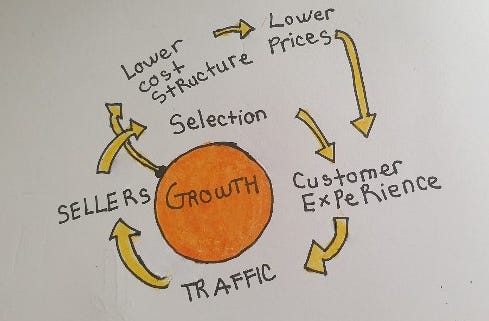
At the heart of Amazon's remarkable growth lies the concept of the Flywheel, which Jeff Bezos famously sketched on a napkin. This powerful strategy was later illustrated as the "Amazon Virtuous Cycle" in a PowerPoint presentation.
Jeff Bezos identified the three most important aspects that would propel Amazon to greatness:
Low prices
Huge selections
Great customer experience
All three aspects converge under the umbrella of "customer obsession". This unwavering focus on delivering exceptional value to customers is the driving force behind Amazon's success.
So how does the Amazon Flywheel work?
Amazon Virtuous Cycle
In the book “The Everything Store: Jeff Bezos and the Age of Amazon,” journalist Brad Stone explains about the “flywheel effect” at Amazon like this: “Lower prices led to more customer visits. More customers increased the volume of sales and attracted more commission-paying third-party sellers to the site. That allowed Amazon to get more out of fixed costs like the fulfillment centers and the servers needed to run the website. This greater efficiency then enabled it to lower prices further. Feed any part of this flywheel, they reasoned, and it should accelerate the loop.”
Let’s break down each component in Amazon’s growth strategy to make it become a part of the flywheel.
Customer Obsession: The Foundation of Amazon's Flywheel
From the outset, Amazon's founder, Jeff Bezos, understood that success rooted on prioritizing customers above all else. This obsession with customer satisfaction underpins every aspect of the flywheel.
“If there’s one reason we have done better than our peers in the Internet space over the last six years, it is because we have been focused like a laser on customer experience, and that really does matter, I think, in any business. It certainly matters online, where word-of-mouth is so very, very powerful.” – Jeff Bezos
By putting customer experience as the top priority, Amazon realized more values to customers by offering Amazon Prime in 2005, focusing on fast and free delivery and more benefits for its customers including exclusive deals, and access to its various streaming contents. Currently there are over 200 million Amazon Prime members worldwide, providing a recurring revenue stream while encouraging customer loyalty and frequent purchases.
Vast Selection and Availability: The Virtuous Cycle of Product Diversity
Amazon's focus on customer satisfaction drives the continuous expansion of its product selection. The company has increased an astonishing range of offerings, from books to electronics, clothing, grocery, household items and more. By catering to diverse customer needs, Amazon attracts a broader audience, increasing customer acquisition and retention.
In 2022, Amazon's product selection exceeded 12 million items worldwide, giving customers unparalleled choice. This vast selection creates a positive feedback loop where more customers are attracted, leading to increased demand for diverse products.
Marketplace and Third-Party Sellers: Expanding the Ecosystem
The Amazon Marketplace plays a pivotal role in the flywheel, acting as a complementary platform for third-party sellers. This extension of the Amazon ecosystem broadens the product catalog, drawing more customers while providing sellers access to a massive customer base.
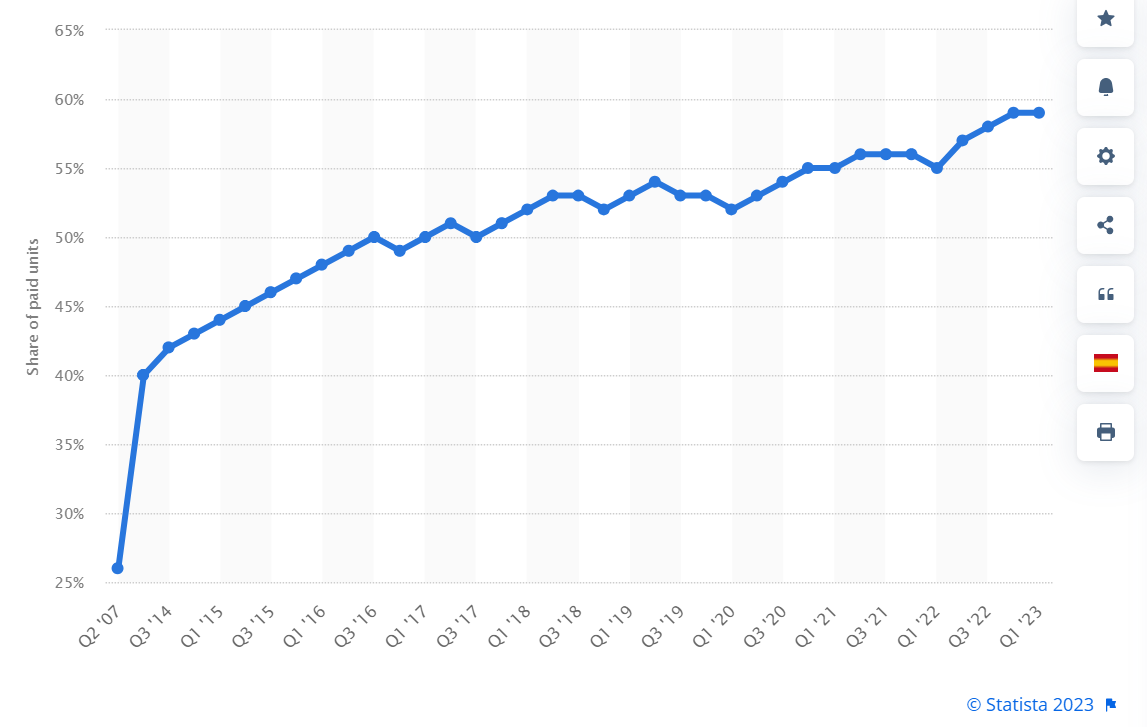
As of the 1st quarter of 2023, third-party sellers accounted for nearly 60% of gross merchandising value on Amazon. This shows the significant role they play in the company's growth, as their presence expands the selection and attracts more customers.
Share of 3rd party’s GMV on Amazon from 2007 to 2023
Competitive Pricing: Fueling the Desire to Purchase
A critical aspect of Amazon's flywheel is its ability to offer competitive prices. The company's extensive network of suppliers and the leverage of advanced algorithms and data analytics enable it to negotiate favorable deals and pass on cost savings to customers. Consequently, competitive pricing bolsters customer trust and encourages more frequent purchases.
A research by Profitero revealed that Amazon consistently offered the lowest prices among major online retailers across various product categories. It helped Amazon to strengthen it customer loyalty and trust. It resulted that a large majority of consumers (89%) are more likely to buy products from Amazon than other e-commerce sites.
Fulfillment and Logistics: The Engine of Customer Delight
Fast and reliable fulfillment is the backbone of Amazon's flywheel in its mission of a customer-centric company. The company's vast network of fulfillment centers and advanced logistics technology ensures swift deliveries to customers, creating a seamless shopping experience. As customers receive their orders quickly and accurately, their satisfaction and trust in Amazon grow.
Instead of relying third party logistic providers, here is how Amazon has built and utilized its fulfillment and logistics capabilities to enhance customer satisfaction.
Fast and Reliable Delivery: Offer same-day or one-day delivery options, or even two-hour delivery in some selective areas, which is made possible through its strategic placement of fulfillment centers. Another contributor to Amazon’s fast delivery options is its fleet of 89 cargo planes for Amazon Air, dedicated to transporting packages across the United States. Amazon also offers Prime Air which is a futuristic drone delivery initiative, aiming to revolutionize last-mile delivery. It offers to use unmanned and electric-powered drones to deliver package directly to customer’s homes in just 30 minutes. It is especially helpful to serve customes in urban areas with congested traffic or remote locations.
Technology and Robotics: The application of cutting-edge technology and robotics has helped Amazon streamline the order processing and reduce time of picking, packing and shipping items. Amazon employs robots equipped with AI and computer vision capabilities to assist with order picking in its fulfillment centers. Automated packaging machines are also used to customize the packaging box sizes for items. The inventory management is powered by machine learning algorithms to predict customer demand more accurately.
Multiple Fulfillment Options: In addition to its own fulfillment centers, Amazon also offers fulfillment services to third-party sellers through its Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program. This allows sellers to store their products in Amazon's warehouses and take advantage of its efficient shipping and handling processes, which ensure the consistent service level for all items sold out.
Innovation and Technology: Pioneering the Future
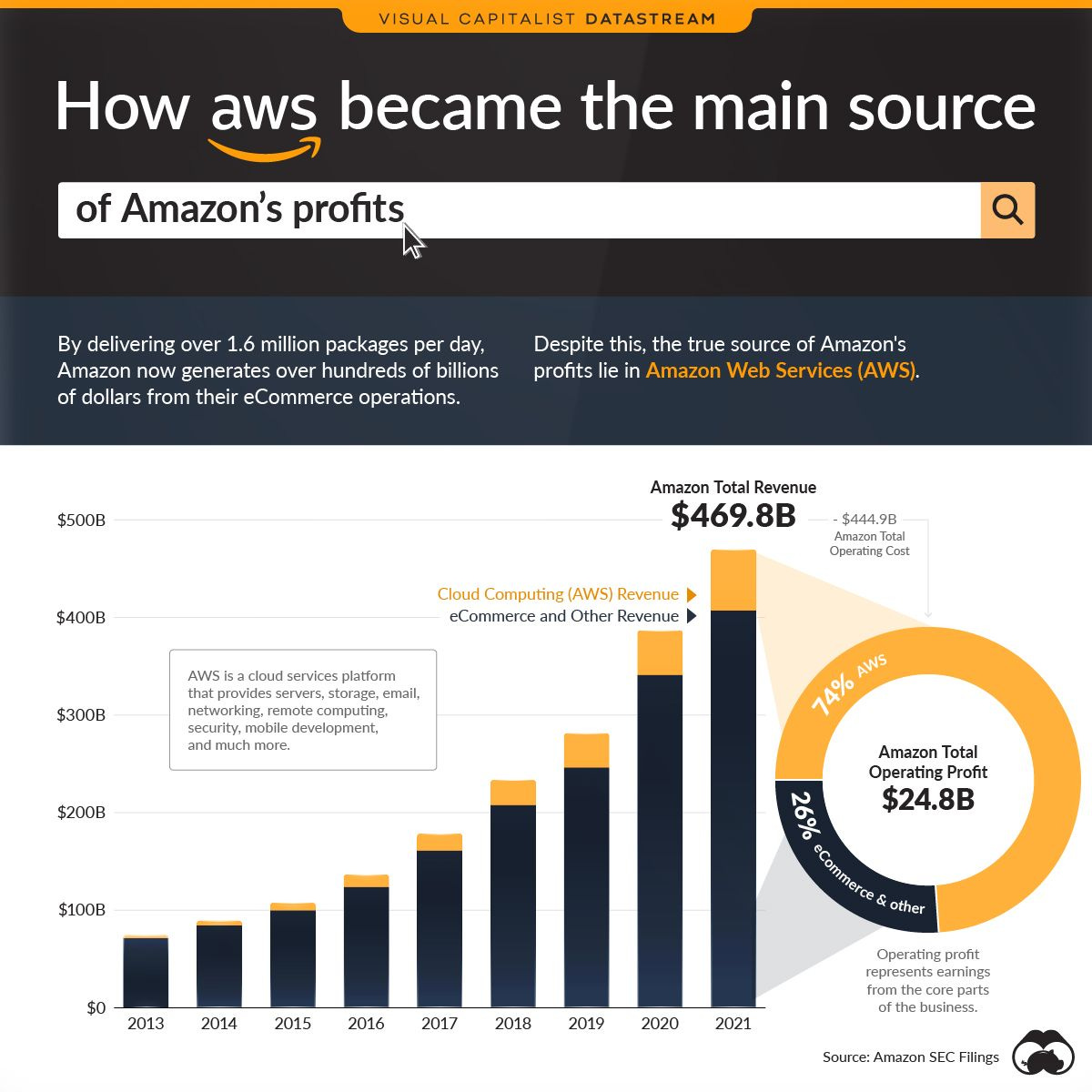
Amazon's unyielding focus on innovation has powered its expansion into various industries including cloud computing, healthcare, entertainment, smart home devices. The company's commitment to investing in cutting-edge technology has led to groundbreaking products and services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Alexa, and Amazon Go, ensuring Amazon remains at the forefront of the tech revolution.
AWS is a prime example of the flywheel effect in action. AWS was launched in 2006 and has grown exponentially since then. Amazon has been running effectively on its flywheel and AWS is the cashcow to drive substantial profits back into Amazon's business, fueling further innovation and growth for the company.
Source: Visual Capitalist
The Amazon flywheel is the proven result to the power of customer obsession, operational excellence, and continuous innovation. In nearly last 30 years, Amazon's relentless pursuit of improving the customer experience, broadening its product selection, offering competitive pricing, and leveraging technology has resulted in outstanding growth trajectory. The flywheel effect continues to propel Amazon forward, shaping its future endeavors and solidifying its position as a global leader in the digital age. As the company keeps refining and amplifying its flywheel, it will be exciting to witness how Amazon continues to transform industries and shape the world of commerce for years to come.
That’s all for today. Till next week!
Cheers,
Do Thi Dieu Thuong


like